Flame treating stands as a captivating alchemy between science and art, where the controlled application of heat transforms surfaces with meticulous precision. From enhancing adhesion properties to enabling artistic endeavors, this technique has garnered attention across industries.
By delving into the historical roots, principles, equipment, chemistry, applications, safety measures, and future prospects of flame treating, we uncover a world of possibilities that bridges the gap between tradition and innovation.
Historical Context: Evolution of Flame Treatment Techniques

Source: brighton-science.com
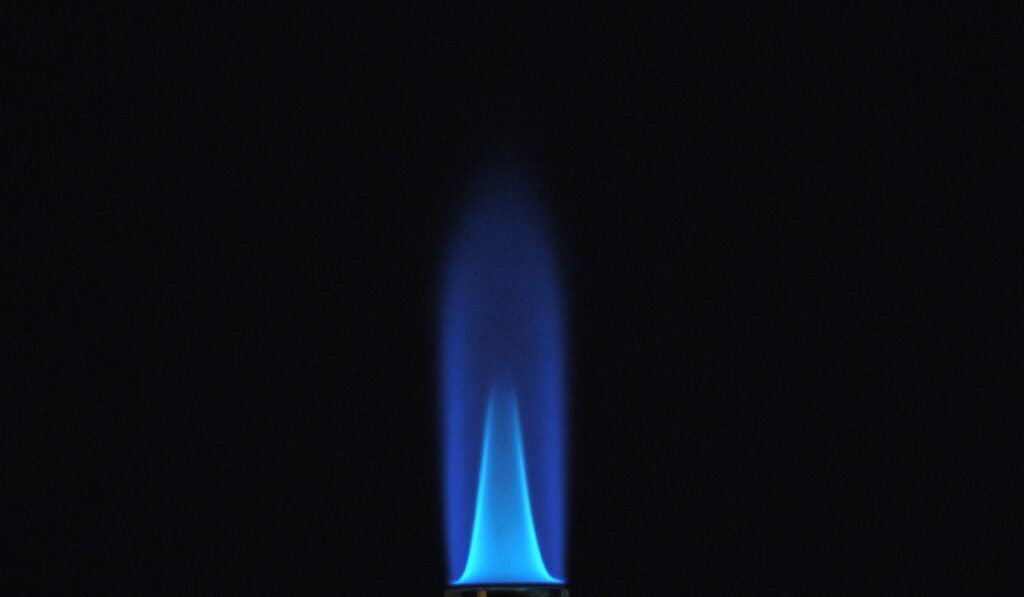
Rooted in ancient metallurgy, flame treatment traces its lineage to early blacksmithing practices. Over time, it found its way into diverse applications, including glasswork, pottery, and metal fabrication. However, it wasn’t until the mid-20th century that controlled flame treatment gained momentum.
This evolution, driven by advancements in technology and understanding of material sciences, including the development of more sophisticated Flame Treating Burners, laid the groundwork for today’s precise and effective flame treatment methods.
Key Principles: Heat’s Role in Precision Modification
Key to treating efficacy is the fundamental principle of heat’s role in precision modification. By subjecting materials to carefully controlled heat, surfaces undergo transformative changes on a molecular level. At elevated temperatures, chemical bonds within the material weaken, allowing for reconfiguration and the creation of reactive sites.
This alteration enhances the surface’s affinity for coatings, adhesives, or inks, leading to improved adhesion and functional properties. The interplay between temperature, exposure time, and distance from the fire dictates the degree of modification, highlighting the meticulous balance required for consistent and desired outcomes.
Through this principle, heat treating unlocks the potential for tailored material enhancements across diverse industries.
Equipment Overview: Tools for Controlled Flame Treatment

Source: enerconind.com
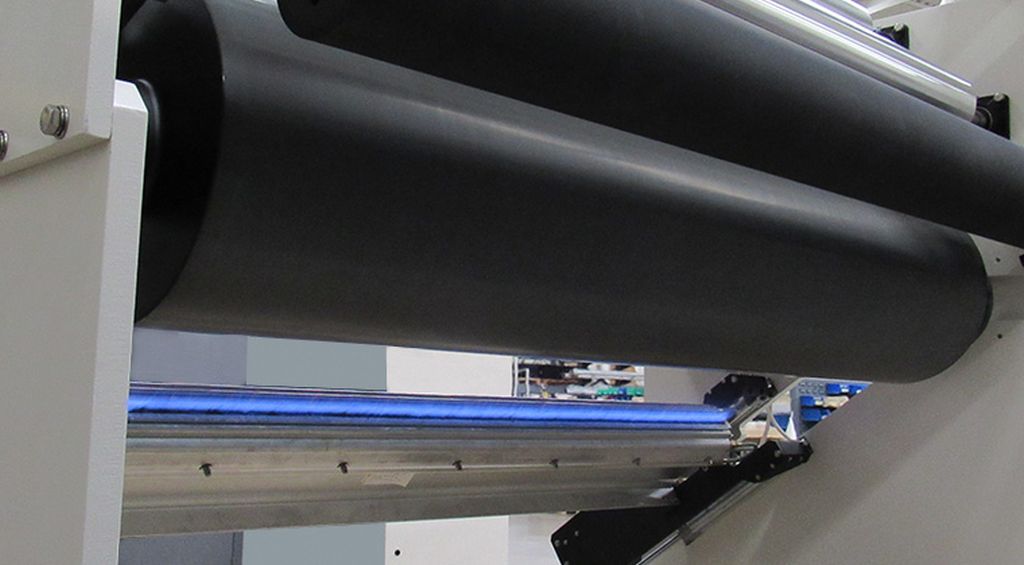
Modern fire control uses specialized tools that guarantee accuracy and security. The equipment used to produce the required heat and energy includes flamethrowers, plasma systems, and corona discharge devices.
These gadgets’ programmable settings enable customized treatments for certain materials and applications. Such adaptability enables sectors from automobiles to electronics to profit from heat ablation.
Surface Chemistry: Molecular Transformations Under High Temperatures
Surface chemistry takes center stage in flame treating, where molecular transformations under high temperatures orchestrate material metamorphosis. As materials encounter intense heat, chemical bonds undergo a delicate dance of breaking and reforming.
This process creates reactive sites on the surface, ready to engage with coatings, adhesives, or inks. These alterations extend beyond the immediate surface, influencing the material’s overall structure and properties.
The thermal energy encourages atoms to realign, leading to enhanced wettability, adhesion, and functional performance. Understanding these intricate molecular changes empowers industries to engineer surfaces with tailored characteristics, opening doors to advanced technologies and applications across sectors like electronics, packaging, and medical devices.
Industrial Applications: Flame Treatment in Manufacturing Processes

Source: flametreaters.com
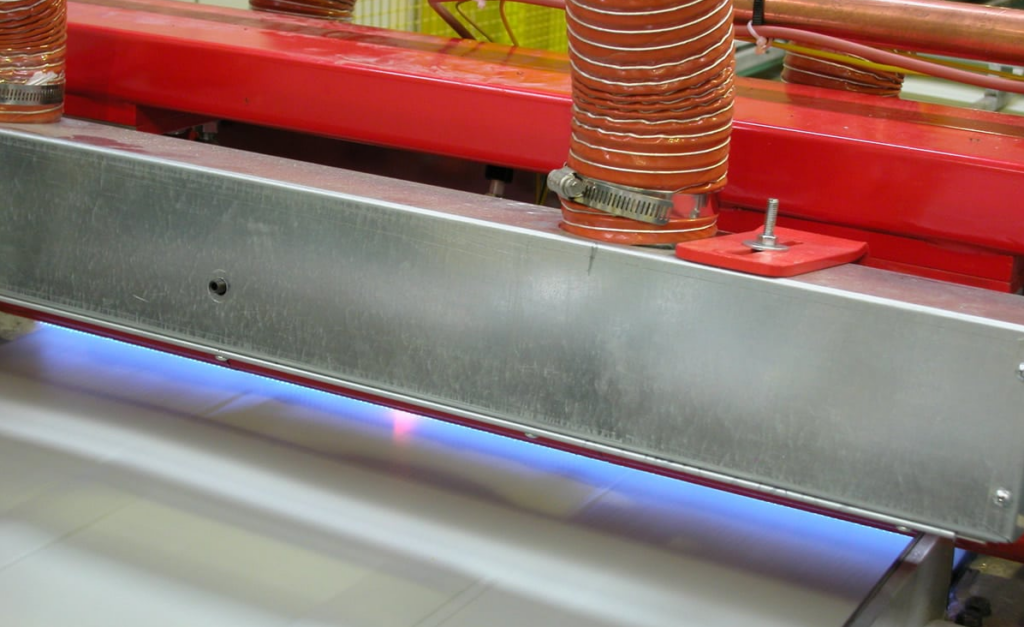
A core stage in many industrial processes is heat treatment. It prepares plastic components for painting in the automobile industry and prepares plastic bottles for labeling in the packaging industry. Printing technology may use this treatment’s capacity to activate surfaces and enhance ink adherence.
Additionally, fire control is used in the medical industry to improve the biocompatibility of implant materials. Its widespread applicability attests to its worth across sectors.
Artistic Potential: Creative Uses in Crafting and Design
Beyond its industrial applications, flame treating ignites a realm of artistic potential, offering creative uses in crafting and design. Craftsmen wield this technique to etch intricate patterns onto glass, manipulate wood textures, and create one-of-a-kind metal finishes.
The controlled application of heat transforms surfaces into canvases, where the play of flames becomes an art form itself. By embracing heat control as an artistic tool, designers bridge tradition with innovation, producing captivating pieces that blend the beauty of craftsmanship with the precision of technology.
This synergy elevates artistic expression, breathing life into furniture, sculptures, and decorative objects, while pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in the world of artistic creation.
Safety Measures: Ensuring Secure Handling of Open Flames
Working with open flames demands meticulous adherence to safety protocols. Adequate ventilation, protective gear, and fire-resistant surroundings are non-negotiable. Proper training in heat application techniques minimizes risks while ensuring consistent results. Safety not only safeguards personnel but also the quality and efficacy of flame-treated materials.
Comparative Methods: Contrasting Flame Treatment with Other Techniques

Source: polymer-surface.com
In the landscape of surface modification, flame treatment is just one player in a diverse ensemble. Thermal methods like heat tunnels and convection ovens, as well as chemical processes like plasma and corona treatment, offer alternatives with unique advantages. Flame treatment’s distinctiveness lies in its ability to combine precision and adaptability, making it a standout choice in situations demanding controlled and versatile surface alterations.
Environmental Impact: Sustainable Practices and Emissions Reduction
As environmental concerns take center stage, the sustainability of manufacturing processes becomes paramount. Flame treating, when executed mindfully, can align with eco-friendly practices. Innovations like energy-efficient burners and cleaner fuel sources contribute to reducing its carbon footprint. Additionally, the ability to enhance coating adhesion reduces material waste, further aligning flame treatment with sustainable principles.
Future Prospects: Advancements and Untapped Possibilities in Flame Treatment
The future brims with exciting prospects, poised for advancements and the exploration of untapped possibilities. As technology and material sciences progress, heat control is set to witness enhanced automation and integration with digital design tools.
This synergy promises to revolutionize precision and efficiency across industries. Collaborations between disciplines might unearth novel applications, from architectural innovations to cutting-edge wearable technology.
Furthermore, the development of new heat sources and burner technologies could refine and diversify the process. With sustainability at the forefront, research into cleaner fuel sources and eco-friendly practices could pave the way for greener methods. As we look ahead, the horizon gleams with innovation, ready to reshape material alteration and creativity on multiple fronts.
Conclusion

Source: innovent-jena.de
In conclusion, the art of flame treating encapsulates the fusion of science, craftsmanship, and innovation. Its historical evolution, precise principles, versatile equipment, transformative chemistry, and broad applications showcase its importance across industries.
Whether it’s revolutionizing manufacturing processes or elevating artistic creations, flame-treating legacy as a powerful and versatile tool is poised to continue shaping the future of material alteration.